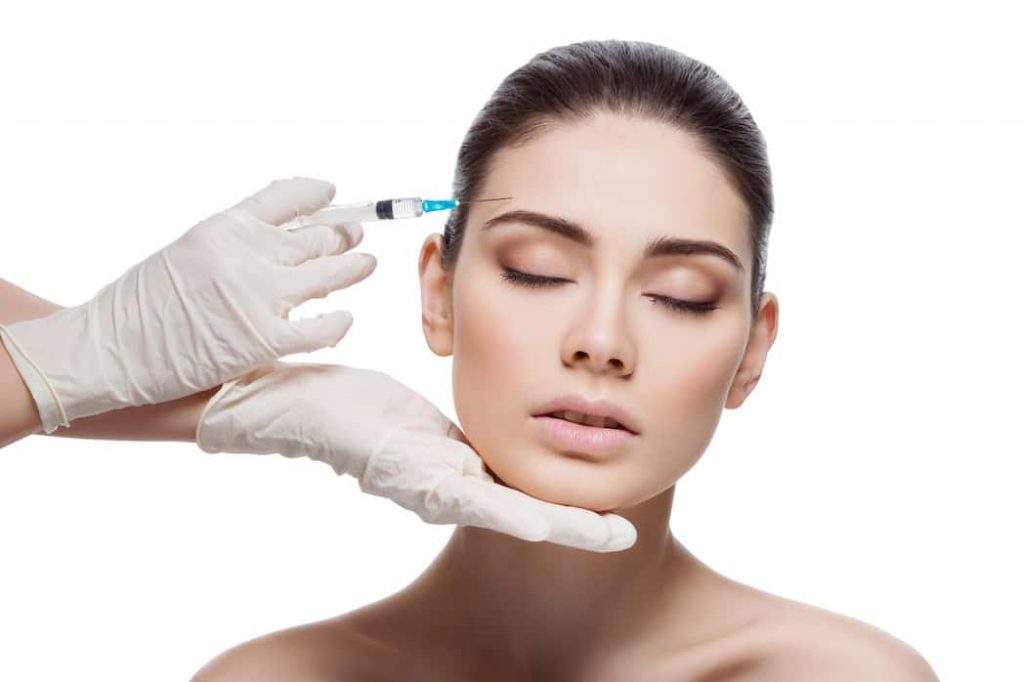
Botox can be injected as medication from botulinum’s toxin type A. The toxin is created by the bacteria Clostridium Botulinum. However, it’s the same toxin that causes botulism (a life-threatening form caused by food poisoning); however, the effects of botulism differ in proportion to the dose and the type of exposure. For instance, Botox is only injected in tiny doses.
In the event of injection, Botox blocks signal from your nerves to the muscles. It stops the muscles targeted from contracting, which may alleviate specific muscular ailments and help improve the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Continue reading to learn more about the security of Botox as well as the most typical uses, possible unwanted side effects to be aware of, and much more.
What Does it Mean, and How is it Functioning?
Botox is commonly referred to for its role as a neurotoxin. The chemicals attack the nervous system and disrupt neurons’ signaling channels, triggering muscles to contract. That is the reason the drug causes paralysis of muscles temporarily.
It is located in the region where nerve endings connect muscle cells. Acetylcholine binds to muscle cell receptors, causing muscle cells to shrink or contract. Botox injections block the release of Acetylcholine, which stops the muscles from contracting. That is the reason why the toxin helps muscles relax.
What types of Beauty Issues can be Treated using Botox?
Botox injections are utilized to treat wrinkles and signs of aging. The treatment can smooth out wrinkles and fine lines across your face, such as:
- Eyebrows.
- Forehead.
- Nose.
- Lips.
- Chin.
- Jawline.
- Neck.
What are Conditions of the Body Treatable with Botox?
Botox injections block nerve signals with chemical substances, which generally signals that because muscles relax. The most well-known application for these injections is to relax facial muscles temporarily. These create wrinkles on the forehead as well as around the eyes. Botox injections are also used to treat illnesses that affect how the body works. Examples include:
- Cervical Dystonia: In this painful condition, the neck muscles relax, which causes your head to turn or turn to an unbearable point.
- Lazy Eyes: The most common reason for lazy eyes could be a lack of strength in the muscle that controls the eye’s movement.
- The Muscles Contract: Some neurological conditions, such as cerebral palsy, can pull your legs toward your center. In certain instances, muscle contractures can be eased through Botox injections.
- Hyperhidrosis: In this condition, it is customary to sweat excessively even when the temperature isn’t scorching or you’re exerting yourself to the max.
- A Persistent Migraine: If you experience migraines that last more than 15 times every month, Botox injections can help decrease the frequency of headaches.
Do you Know Who is Elected not to Receive Botox Injections?
Botox injections are relatively secure. But, it isn’t recommended to get this procedure if you’re Expecting or breastfeeding or if you have:
- Neuromuscular disease.
- Eyelids that are drooping (ptosis).
- Facial muscles are weak.
Is Botox Harmful?
With a topical anesthetic using a topical anesthetic, a Botox procedure is painless. It isn’t too bad if you don’t have a pain-killing medication, and it’s possible to feel a tiny squeeze. The injections are quick. With help from an expert doctor, you may not know they occur.
Many people experience pain from Botox due to fear of needles or negative memories of receiving vaccinations. It’s a good thing to know that Botox needles may be tiny. They’re the same size needles that patients who have diabetes inject insulin. A frequent adverse consequence associated with Botox can be minor bruises that might be tender; however, they will subside quickly.
What can I expect from the Botox procedure?
The doctor employs a fine needle to inject tiny amounts of Botox into the treatment area. Based on the problem, you could receive several injections at different locations. What else do you need to be aware of about Botox treatment:
- Botox is an in-office procedure. It is possible to return home on the same day.
- The discomfort is typically minimal. The injections could cause pain and cause discomfort, but the procedure can be completed quickly. Your doctor may use topical nerve-numbing cream on your skin before giving injections.
- It is possible to receive anesthesia. If you’re receiving injections to treat an active bladder, you could receive regional or local anesthesia.
How Is a Botox Procedure Done?
A procedure like Botox requires only a few minutes. There is no need for anesthesia. The doctor uses a tiny needle that injects Botox into specific muscles. There is just a little discomfort. It typically takes 7 to 14 days for the procedure to fully effect. It’s recommended to avoid drinking alcohol beginning at least one week before the process.
Also, you should quit drinking aspirin and anti-inflammatory medication two weeks before the procedure to avoid bruising. Do not rub the injection site for 24 hours to ensure you don’t spread Botox into other areas. The doctor might also advise that you remain in a straight position for four hours following the injections and then rest for a day from doing any exercise.